|
|
On the most important:
|
Science reporting session

|

Abstracts 2011

Abstracts 2012

Abstracts 2013

Abstracts 2014
|

He main directions of development of hydrogen energy (review)

Hydrogen energy: storage and transportation of hydrogen (review)
|

Monograph.
Basic problem of hydrogen energy.
|
|
|
|
|
Creating a multi-layer assembly of fuel cell components, development of forming and sintering methods
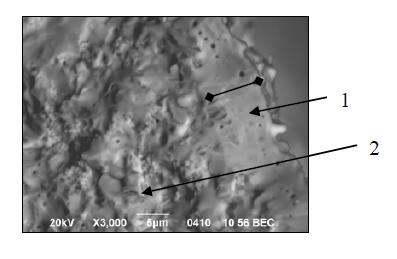
Zirconia nanopowder , tubular fuel cell and its structure: 1 – anode layer, 2 - electrolyte layer, 3 - cathode layer.
Area of applications
Energetic
Brief description
The project aims to develop technological bases of production materials and components of fuel cells.
All materials and fuel cell components designed and manufactured in the material science department of DonIPh&E NAS of Ukraine.
The technologies for production of weak agglomerated nanopowders for all elements of the fuel cell were made for: electrolyte - based on zirconium oxide stabilized by multivalent dopants, anode - nanocomposite with composition of ZrO2-NiO and cathode - nanocomposite with composition ZrO2 - LaSrMnO3 (LaSrCoO3). The technology of forming and sintering of tubular fuel cells up to 200 mm and 6-8 mm section was done.
The optimal technological regimes of forming, sintering and recovery of the fuel cell was determined.
Expected results
Sintering at temperatures 1400 - 1500ºC was obtained ceramic samples of the anode, the anode-electrolyte bilayer assembly in the form of tubes with a diameter of 6 - 8 mm and a length of 150-200 mm. Control of the level of pressure compaction can vary the amount of anode porosity. It was established that the structure, phase and chemical composition of fuel cell elements correspond to given characteristics.
It was established that the level of ionic conductivity on the volume of grain at 600ºC is (1-3) x 10 -1Om -1m -1 and weakly depends on the type of dopants.
Advantages
It was established that only when using the hydrostatic pressing and co-sintering of nanopowders the bilayer assembly of anode and electrolyte materials of tubular form was made. That assembly provided a regular cylindrical shape and the necessary strength and porosity of the supporting anode layer and a small thickness (10 - 20 microns) and high density of the electrolyte layer in comparison with other methods.
Competitors
Siemens Power Corporation;
Bloom Energy, Aqumetric, Staxera.
Project development
As a result of the work the technological regimes of obtaining of bilayer assembly of tubular shape with supporting anode from nanopowders were worked out. The fuel cell with the required level of porosity anode and a thin gas-tight electrolyte was made. Cathode layer was deposited by spraying a suspension of nanopowder composition ZrO2 - LaSrMnO3 and sintering at 1100-1200ºC.
Intellectual property
The basic version of the technology of obtaining nanopowders patented in Ukraine for invention "The process of obtaining powders of oxides" №81966 / TE Konstantinova, Pylypenko MP, Oleksienko VI Danilenko, IA / own. DonIPhE - Application a200601880 number of 21.02.2006r. Bull. №4 from 25.02.2008.
Contact information
Executor: Donetsk Institute of Physics and Engineering named after O.O. Galkin National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine
Project №38 "The development of new highly efficient materials with functional and structural properties and the creation of experimental samples of oxide-ceramic fuel cells based on ZrO2"
Contact person:
Konstantinova Tetyana
Е-mail: matscidep@aim.com
|